The future perfect tense is an essential part of English grammar, used to express actions or events that will be completed by a particular time in the future. It helps in describing actions that are expected to finish before another event or deadline in the future. In this article, we will provide a detailed and structured guide to understanding and using the future perfect tense effectively, with examples, comparisons, and key points.
What is the Future Perfect Tense?
The future perfect tense refers to a grammatical structure used to describe actions that will have been completed before a specific point in the future. Unlike the simple future tense, which describes events occurring at any point in the future, the future perfect tense emphasizes the completion of an action by a certain time.
Key Features:
-
Indicates completion of an action or event in the future before a specific moment.
-
Typically uses the structure “will have + past participle.”
-
It can refer to a specific point in time or another future event by which the action is expected to be completed.
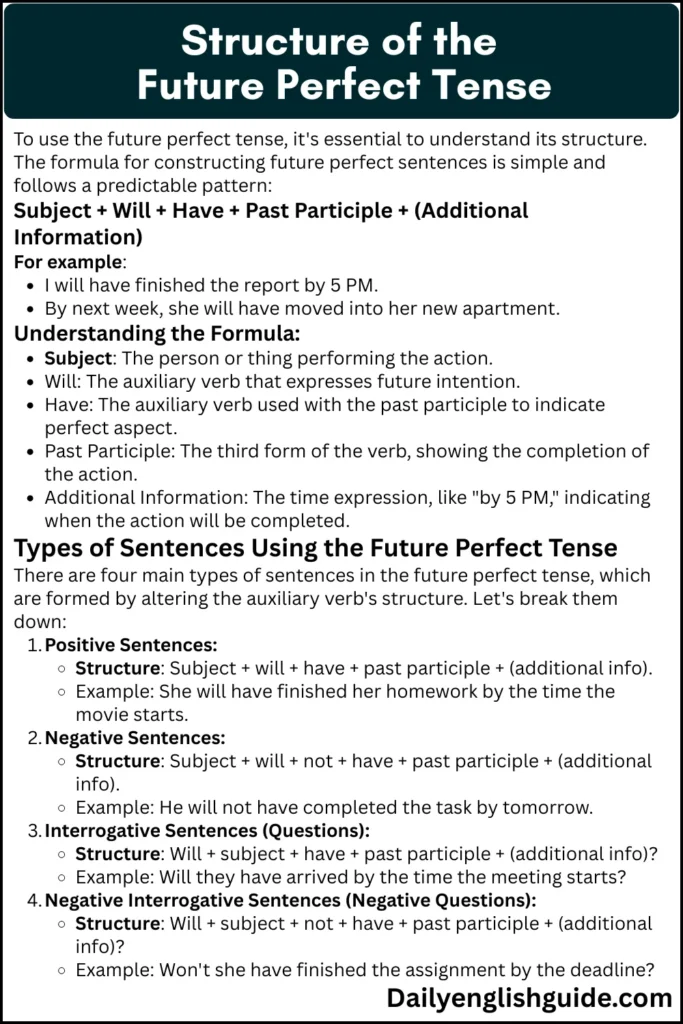
Structure of the Future Perfect Tense
To use the future perfect tense, it’s essential to understand its structure. The formula for constructing future perfect sentences is simple and follows a predictable pattern:
Subject + Will + Have + Past Participle + (Additional Information)
For example:
-
I will have finished the report by 5 PM.
-
By next week, she will have moved into her new apartment.
Understanding the Formula:
-
Subject: The person or thing performing the action.
-
Will: The auxiliary verb that expresses future intention.
-
Have: The auxiliary verb used with the past participle to indicate perfect aspect.
-
Past Participle: The third form of the verb, showing the completion of the action.
-
Additional Information: The time expression, like “by 5 PM,” indicating when the action will be completed.
Types of Sentences Using the Future Perfect Tense
There are four main types of sentences in the future perfect tense, which are formed by altering the auxiliary verb’s structure. Let’s break them down:
-
Positive Sentences:
-
Structure: Subject + will + have + past participle + (additional info).
-
Example: She will have finished her homework by the time the movie starts.
-
-
Negative Sentences:
-
Structure: Subject + will + not + have + past participle + (additional info).
-
Example: He will not have completed the task by tomorrow.
-
-
Interrogative Sentences (Questions):
-
Structure: Will + subject + have + past participle + (additional info)?
-
Example: Will they have arrived by the time the meeting starts?
-
-
Negative Interrogative Sentences (Negative Questions):
-
Structure: Will + subject + not + have + past participle + (additional info)?
-
Example: Won’t she have finished the assignment by the deadline?
-
Understanding these variations allows for precise communication in both affirmative and questioning forms.
Examples of the Future Perfect Tense in Action
To fully grasp how the future perfect tense works, let’s explore a few real-world examples. These will help illustrate how this tense is used to refer to actions completed by a future time or event.
Referring to Completion Before a Specific Time:
-
She will have finished the presentation by the time the meeting begins.
-
By 2025, we will have completed the new building project.
In these examples, the future perfect tense is used to express actions that will be finished before another event in the future.
Expressing Completion Before Another Event:
-
The flight will have landed by the time we reach the airport.
-
By the time I return, they will have left for the conference.
These sentences show the use of the future perfect tense to highlight actions that will be completed before another action or event happens.
Making Predictions or Convictions About the Future:
-
I believe she will have learned the new software by the end of this week.
-
By the time you arrive, I will have eaten dinner.
In these cases, the future perfect tense expresses a belief or assumption about what will happen by a certain future time.
Key Points to Remember About the Future Perfect Tense
When using the future perfect tense, it’s important to keep the following points in mind:
-
Future time references are crucial: The future perfect tense requires a clear indication of when the action will be completed. You can use time phrases like by tomorrow, before noon, by the time, and by the end of the week.
-
Always use “will have” for positive and negative sentences, followed by the past participle of the main verb.
-
Irregular verbs: Just like other perfect tenses, the future perfect tense also uses past participles, which for irregular verbs do not follow the “ed” rule. For example, “go” becomes “gone,” “eat” becomes “eaten,” etc.
Adverbs and Time Expressions with the Future Perfect Tense
-
Before: “I will have finished the book before the meeting starts.”
-
By the time: “By the time you arrive, we will have completed the survey.”
-
By (a specific time): “We will have reached our destination by 10 PM.”
-
Until: “He will have left until you return.”
-
By the end of: “By the end of the year, we will have launched the product.”
The future perfect tense emphasizes actions that will be completed before or by specific times or events, making it a useful tool for planning and prediction.
Future Perfect Tense: Detailed Explanation and Usage
In English grammar, the future perfect tense plays a vital role in conveying actions or events that will be completed before a specific time or event in the future. It’s a tense that allows you to express the completion of an action relative to a future point in time. In this section, we’ll dive deeper into its usage, examples, and how to form sentences in this tense.
Understanding the Formula of the Future Perfect Tense
To effectively use the future perfect tense, it’s important to understand the structure. The formula is simple yet powerful and helps in clearly expressing ideas about future actions that will be completed before a certain time or event.
Formula:
-
Subject + will + have + past participle + (additional time expression)
Breakdown of the Formula:
-
Subject: Refers to the noun or pronoun performing the action (e.g., I, they, she).
-
Will: The auxiliary verb indicating the future tense.
-
Have: The auxiliary verb used to form the perfect aspect.
-
Past Participle: The third form of the verb, showing that the action has been completed (e.g., eaten, written, finished).
-
Time Expression: Provides information about when the action will be completed (e.g., by 5 PM, before the end of the day).
For example:
-
I will have completed the project by tomorrow.
-
By next year, they will have achieved their goals.

Positive, Negative, and Interrogative Sentences
When forming sentences with the future perfect tense, it’s important to note the structure for positive, negative, and interrogative forms.
1. Positive Sentences
The structure for positive sentences in the future perfect tense is as follows:
-
Subject + will + have + past participle + (additional time info)
Example:
-
They will have finished the work by 3 PM.
-
By the end of the month, I will have saved enough money for the trip.
2. Negative Sentences
To create negative sentences, the auxiliary verb “will” is combined with “not,” making it “won’t” (the contracted form of “will not”):
-
Subject + will + not + have + past participle + (additional time info)
Example:
-
He won’t have completed the task by the deadline.
-
We won’t have visited all the museums by the time the tour ends.
3. Interrogative Sentences
When forming questions, the auxiliary verb “will” comes before the subject:
-
Will + subject + have + past participle + (additional time info)?
Example:
-
Will she have finished the report by the time the meeting starts?
-
Will you have completed the assignment before the deadline?
4. Negative Interrogative Sentences
Negative interrogative sentences are formed by placing “will not” (won’t) before the subject:
-
Will + subject + not + have + past participle + (additional time info)?
Example:
-
Won’t they have finished their work by tomorrow?
-
Won’t I have read the book before the event?
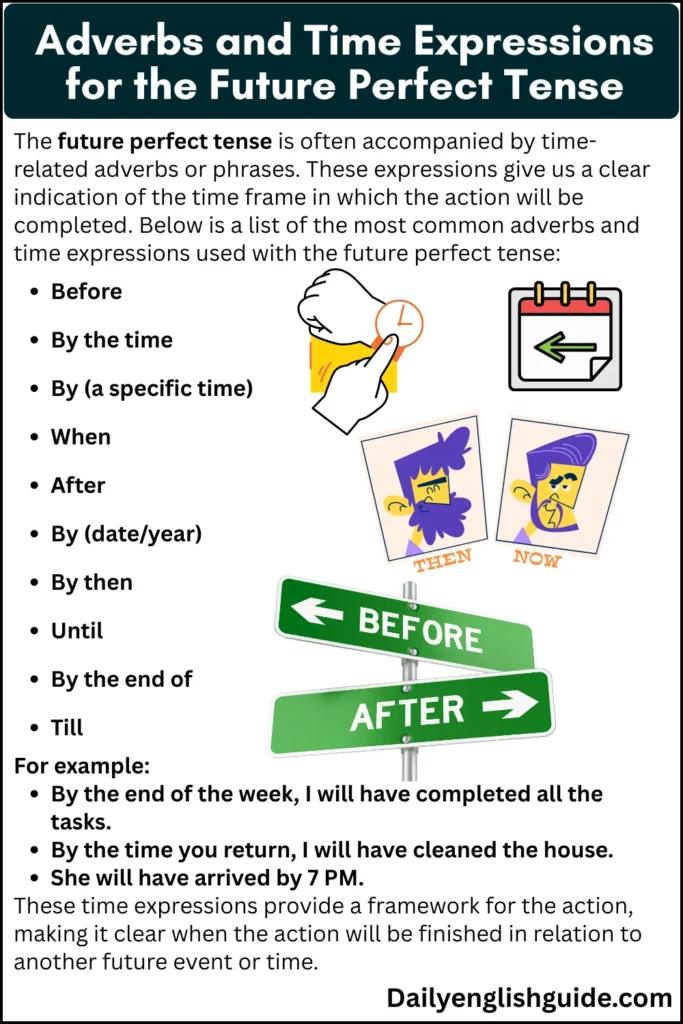
Key Adverbs and Time Expressions for the Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense is often accompanied by time-related adverbs or phrases. These expressions give us a clear indication of the time frame in which the action will be completed. Below is a list of the most common adverbs and time expressions used with the future perfect tense:
-
Before
-
By the time
-
By (a specific time)
-
When
-
After
-
By (date/year)
-
By then
-
Until
-
By the end of
-
Till
For example:
-
By the end of the week, I will have completed all the tasks.
-
By the time you return, I will have cleaned the house.
-
She will have arrived by 7 PM.
These time expressions provide a framework for the action, making it clear when the action will be finished in relation to another future event or time.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
While the future perfect tense is relatively straightforward, it’s easy to make mistakes when using it. Here are a few common errors learners make and how to avoid them:
1. Incorrect Use of Time Expressions
Many students mistakenly omit the necessary time expressions. Always remember that the future perfect tense requires a clear indication of when the action will be completed. Without it, the meaning can be unclear.
Incorrect:
-
I will have finished the report. (No time frame provided)
Correct:
-
I will have finished the report by tomorrow. (Specific time frame included)
2. Confusing with Future Simple
The future perfect tense is often confused with the simple future tense. The difference lies in the completion of the action. The future simple describes events that will happen at some point in the future, while the future perfect describes events that will be completed before a specific time or event in the future.
Incorrect:
-
I will finish the report by tomorrow. (This is future simple, not future perfect.)
Correct:
-
I will have finished the report by tomorrow. (This indicates the action will be completed by a specific time.)
When to Use the Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense is used in a variety of contexts, particularly when we want to refer to actions that will be completed by a certain time in the future. Here are the main situations where the future perfect tense is applicable:
-
To express actions that will be completed before a certain time in the future:
-
Example: By next year, I will have traveled to five different countries.
-
-
To indicate actions that will be completed before another event in the future:
-
Example: The guests will have arrived by the time the ceremony starts.
-
-
To express certainty or assumptions about the completion of actions in the future:
-
Example: By the time you come back, I will have finished cleaning the house.
-
Comparing the Future Perfect Tense with Other Tenses
In English, different tenses serve to convey actions or events occurring at various times. The future perfect tense, being a more specific form of future tense, is often compared with other tenses that deal with the future. Understanding these comparisons will help you choose the right tense to express your ideas clearly.
Future Perfect Tense vs. Simple Future Tense
One of the most common areas of confusion for learners is differentiating between the future perfect tense and the simple future tense. While both are used to talk about actions happening in the future, they serve different purposes.
| Feature | Simple Future Tense | Future Perfect Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Refers to actions that will happen at a point in the future. | Refers to actions that will be completed before a certain time or event in the future. |
| Example | I will travel to Paris next summer. | I will have traveled to Paris by next summer. |
| Time Frame | Not linked to a specific time; just an event in the future. | Specifies when the action will be completed relative to another event or time. |
Key Difference: The simple future tense is used when there is no emphasis on completion by a specific time, while the future perfect tense is used to highlight the completion of an action by a particular future time.
Future Perfect Tense vs. Present Perfect Tense
Another common confusion arises when learners compare the future perfect tense with the present perfect tense. Both tenses involve actions that have been completed, but they differ significantly in the time frame.
| Feature | Present Perfect Tense | Future Perfect Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Refers to actions completed at an unspecified time before now. | Refers to actions that will be completed before a specific future time. |
| Example | I have eaten lunch already. | I will have eaten lunch by 2 PM tomorrow. |
| Time Frame | Unspecified past time, often with a link to the present. | Completion before a future time or event. |
Key Difference: The present perfect tense in the past, while the future perfect tense deals with actions that will be completed in the future.
Practical Uses of the Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense is most commonly used in contexts that involve planning, predictions, deadlines, and assumptions. Here’s a breakdown of different scenarios where the future perfect tense can be applied:
1. Expressing Actions Completed Before a Future Time
The future perfect tense is ideal for talking about actions that will be finished before a specific moment in the future. For example:
-
Example: By the time you return, we will have moved into the new house.
2. Talking About Events That Will Happen Before Another Event
The future perfect tense is useful when referring to an action that will be completed before another event occurs. This helps clarify the sequence of events:
-
Example: The train will have left by the time we reach the station.
3. Making Predictions or Assumptions About the Future
This tense can be used to express assumptions or predictions about the future based on current knowledge or logical reasoning:
-
Example: By next year, the company will have expanded its operations to three new cities.
4. Setting Deadlines or Time Frames for Projects
In business, education, and everyday life, the future perfect tense can be used to indicate when something will be completed, especially in professional settings:
-
Example: We will have finished the report by the end of the day.
How to Master the Future Perfect Tense: Tips and Practice
Mastering the future perfect tense requires consistent practice and understanding of its structure. Here are a few practical tips and exercises to help you improve your usage of this tense:
1. Focus on Time Expressions
The key to using the future perfect tense correctly lies in understanding time references. Always make sure you include a specific time or event in your sentences. Without a time reference, the future perfect tense may sound incomplete.
2. Practice with Examples
The best way to internalize the future perfect tense is by practicing with various examples. You can write sentences describing actions that will be completed by specific future times or events.
3. Use Timeline Visuals
Drawing a timeline can help visualize when actions will be completed. This can be particularly helpful when working with future perfect tense to distinguish when one event will be completed relative to another event in the future.
4. Test Your Knowledge
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the future perfect tense. Here are some practice sentences:
-
By next week, I __________ (finish) my project.
-
She __________ (leave) by the time you arrive at the airport.
-
Will they __________ (complete) the task by the deadline?
Answers:
-
will have finished
-
will have left
-
have completed
