Interjections are one of the most dynamic and expressive parts of speech in the English language. They are words or phrases that express strong emotions, reactions, or sudden bursts of feeling. From exclamations of surprise to outbursts of frustration, interjections convey more than just meaning—they carry tone, mood, and intensity, often without needing any further explanation.
This article will guide you through the essentials of interjections, including what they are, how they function, and how to use them effectively in sentences. We will cover key definitions, examples, punctuation rules, and provide practical tips for mastering this expressive element of language.
What Are Interjections?
An interjection is a word, phrase, or sound that is used to express a spontaneous or emotional reaction. It does not form part of the grammatical structure of a sentence and can stand alone. Typically, interjections serve to convey a quick reaction to something, whether it be surprise, joy, pain, anger, or disbelief.
Unlike other parts of speech, interjections are not used to connect, modify, or describe other words in a sentence. Instead, they act as standalone exclamations that provide insight into the speaker’s emotions or state of mind. Interjections can appear at any point in a sentence but are most commonly placed at the beginning.
For example:
-
“Wow! That was an incredible performance.”
-
“Ouch! That hurt!”
Here, the interjections “wow” and “ouch” are not tied to any subject or verb but stand alone to convey emotion.
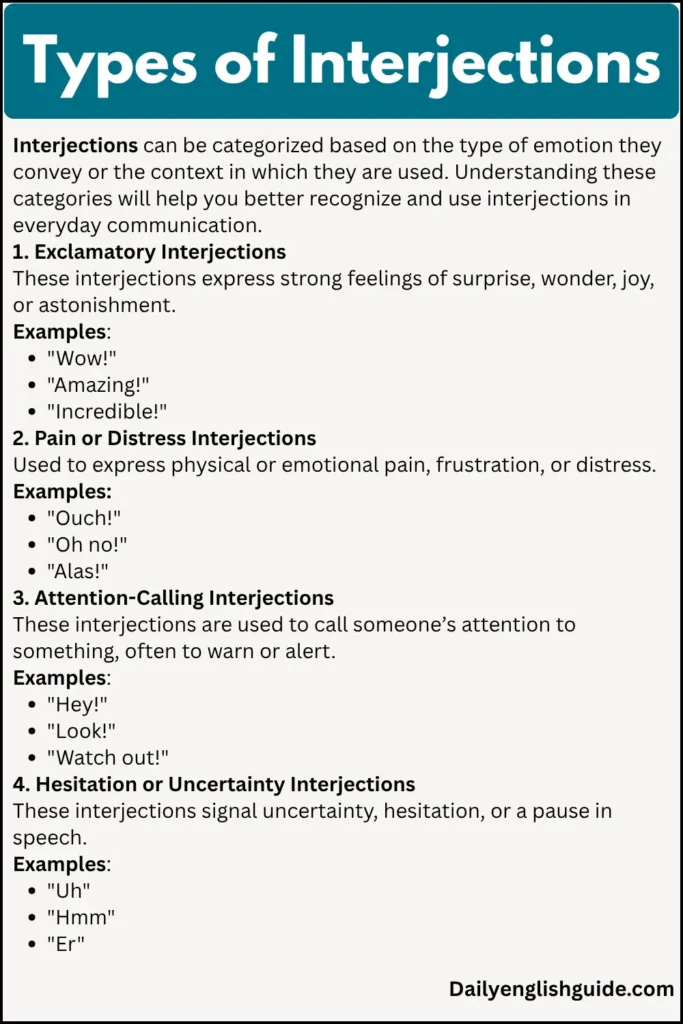
Types of Interjections
Interjections can be categorized based on the type of emotion they convey or the context in which they are used. Understanding these categories will help you better recognize and use interjections in everyday communication.
1. Exclamatory Interjections
These interjections express strong feelings of surprise, wonder, joy, or astonishment.
Examples:
-
“Wow!”
-
“Amazing!”
-
“Incredible!”
2. Pain or Distress Interjections
Used to express physical or emotional pain, frustration, or distress.
Examples:
-
“Ouch!”
-
“Oh no!”
-
“Alas!”
3. Attention-Calling Interjections
These interjections are used to call someone’s attention to something, often to warn or alert.
Examples:
-
“Hey!”
-
“Look!”
-
“Watch out!”
4. Hesitation or Uncertainty Interjections
These interjections signal uncertainty, hesitation, or a pause in speech.
Examples:
-
“Uh”
-
“Hmm”
-
“Er”
5. Greeting Interjections
Interjections used for greetings, farewells, or acknowledgment.
Examples:
-
“Hello!”
-
“Goodbye!”
-
“Hi!”
6. Surprise or Disbelief Interjections
These interjections express shock, surprise, or disbelief at something unexpected.
Examples:
-
“Oh my God!”
-
“What!”
-
“No way!”
Definition of an Interjection
To give a more formal definition, an interjection is often described as:
-
Oxford Learner’s Dictionary: “A short sound, word, or phrase spoken suddenly to express an emotion.”
-
Cambridge Dictionary: “A word that is used to show a short sudden expression of emotion.”
-
Merriam-Webster Dictionary: “A word or phrase used in exclamation.”
-
Macmillan Dictionary: “A word or phrase used for expressing a strong emotion such as surprise or anger.”
Although these definitions differ slightly in phrasing, they all highlight the core function of interjections as vehicles for expressing sudden emotions or reactions.
Importance of Interjections in Language
Interjections are not only expressive but also essential for communication. Here’s why they matter:
1. Conveying Emotion
Interjections are the most direct way to convey emotions in speech, offering a glimpse into the speaker’s immediate feelings. Without them, conversations would lose much of their emotional richness.
2. Creating Emphasis
Interjections help emphasize certain points, often providing context or intensity to a statement. For example, when someone says, “Oh no! I forgot my keys,” the interjection amplifies the sense of distress.
3. Building Rapport in Conversation
In informal settings, interjections can make conversations feel more natural and engaging. They help speakers react to what others are saying and create an environment of shared understanding.
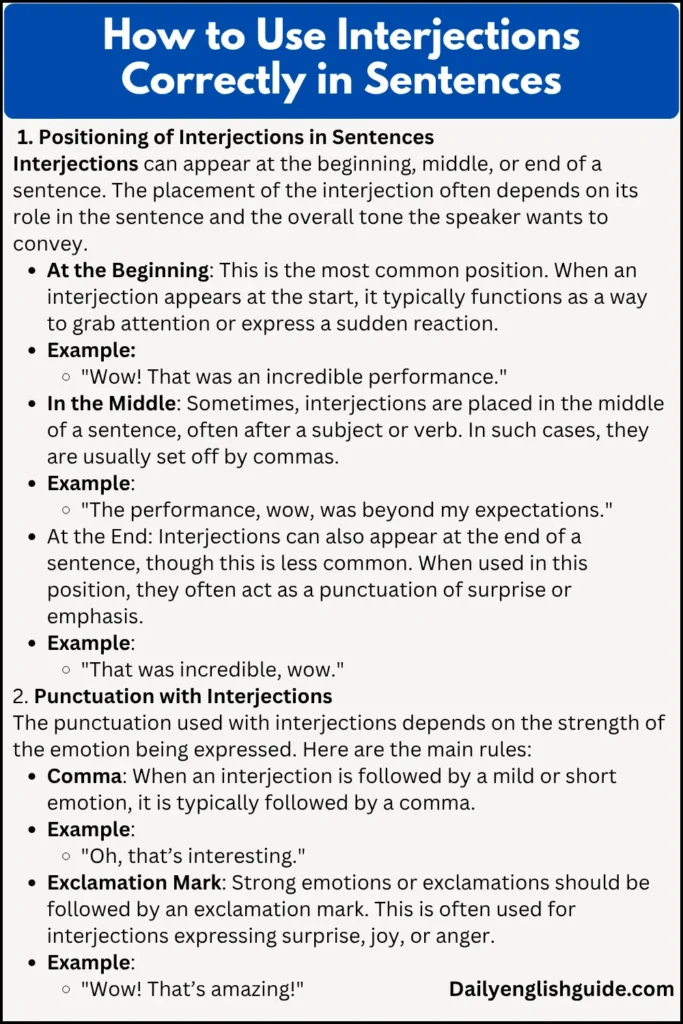
How to Use Interjections Correctly in Sentences
Interjections are versatile, but they come with certain rules regarding their placement and punctuation. Understanding how and when to use them can significantly enhance the clarity and impact of your communication. Here’s a breakdown of the essential guidelines for using interjections in different contexts.
1. Positioning of Interjections in Sentences
Interjections can appear at the beginning, middle, or end of a sentence. The placement of the interjection often depends on its role in the sentence and the overall tone the speaker wants to convey.
-
At the Beginning: This is the most common position. When an interjection appears at the start, it typically functions as a way to grab attention or express a sudden reaction.
Example:
-
“Wow! That was an incredible performance.”
-
-
In the Middle: Sometimes, interjections are placed in the middle of a sentence, often after a subject or verb. In such cases, they are usually set off by commas.
Example:
-
“The performance, wow, was beyond my expectations.”
-
-
At the End: Interjections can also appear at the end of a sentence, though this is less common. When used in this position, they often act as a punctuation of surprise or emphasis.
Example:
-
“That was incredible, wow.”
-
2. Punctuation with Interjections
The punctuation used with interjections depends on the strength of the emotion being expressed. Here are the main rules:
-
Comma: When an interjection is followed by a mild or short emotion, it is typically followed by a comma.
Example:
-
“Oh, that’s interesting.”
-
-
Exclamation Mark: Strong emotions or exclamations should be followed by an exclamation mark. This is often used for interjections expressing surprise, joy, or anger.
Example:
-
“Wow! That’s amazing!”
-
-
Period or Question Mark: When an interjection is used in a more neutral tone, especially in a rhetorical question, a period or question mark may be used.
Example:
-
“Hmm, I’m not sure.”
-
“Uh, do you mean it?”
-
3. When to Avoid Overuse of Interjections
While interjections can be powerful in communication, overusing them can diminish their impact and make the speaker appear overly dramatic or emotional. Particularly in formal writing or professional settings, it’s essential to use interjections sparingly.
For example:
-
Instead of saying, “Oh, wow, I can’t believe this, wow,” you might say, “I can’t believe this.”
In formal writing, it is best to limit the use of interjections to instances where they genuinely add to the meaning or emotional impact of the message.
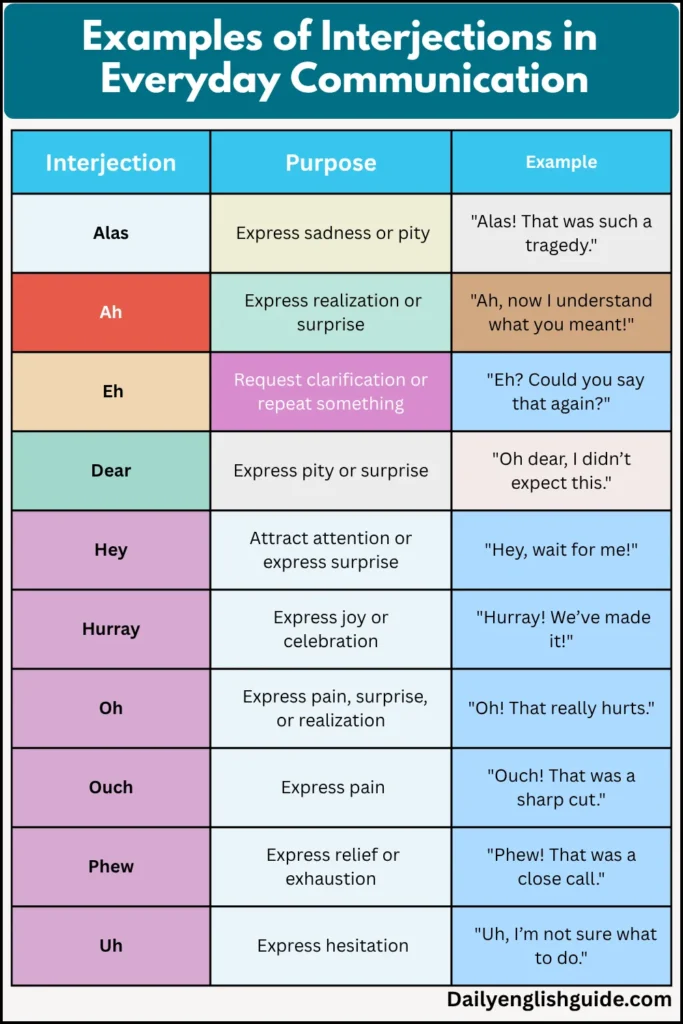
Examples of Interjections in Everyday Communication
Interjections play a significant role in our daily conversations, whether it’s expressing surprise, joy, pain, or excitement. Here is a curated list of common interjections that you can use to make your speech more lively and engaging.
| Interjection | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Alas | Express sadness or pity | “Alas! That was such a tragedy.” |
| Ah | Express realization or surprise | “Ah, now I understand what you meant!” |
| Eh | Request clarification or repeat something | “Eh? Could you say that again?” |
| Dear | Express pity or surprise | “Oh dear, I didn’t expect this.” |
| Hey | Attract attention or express surprise | “Hey, wait for me!” |
| Hurray | Express joy or celebration | “Hurray! We’ve made it!” |
| Oh | Express pain, surprise, or realization | “Oh! That really hurts.” |
| Ouch | Express pain | “Ouch! That was a sharp cut.” |
| Phew | Express relief or exhaustion | “Phew! That was a close call.” |
| Uh | Express hesitation | “Uh, I’m not sure what to do.” |
| Well | Begin a statement or thought | “Well, that’s something to think about.” |
| Wow | Express amazement or admiration | “Wow! That’s the best thing I’ve ever seen!” |
| Yippee | Express excitement or joy | “Yippee! We’re going to the beach!” |
This list provides a practical guide for incorporating interjections into everyday speech to convey the right emotion.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Interjections
Although interjections are a powerful tool for adding expression to speech, they can be misused or overused. Knowing the common mistakes that speakers make with interjections will help you avoid them and ensure that your communication is both effective and appropriate.
1. Overuse in Formal Writing
Interjections are typically more appropriate in informal speech or writing. Overusing them in formal contexts, such as academic papers, business correspondence, or professional presentations, can make you appear unprofessional or overly emotional.
For instance:
-
Incorrect: “Uh, I believe the data is incorrect, ah, we need to verify it.”
-
Correct: “I believe the data is incorrect and needs to be verified.”
In formal writing, it’s best to limit interjections to cases where they truly contribute to the meaning or tone.
2. Improper Punctuation
The punctuation used with interjections is crucial to conveying the correct emotion. Many speakers and writers make the mistake of either over-punctuating or under-punctuating interjections, which can lead to confusion about the intended tone.
For example:
-
Incorrect: “Wow, that was amazing.”
-
Correct: “Wow! That was amazing.”
The exclamation mark here is important to emphasize the surprise and excitement.
3. Misplaced Interjections
Sometimes, interjections are placed awkwardly in sentences, disrupting the flow or making the sentence harder to understand. This can happen if the interjection is inserted in the wrong position within a sentence or when there is no clear emotional context for its use.
For example:
-
Incorrect: “That performance, wow, was spectacular.”
-
Correct: “Wow, that performance was spectacular.”
By placing the interjection at the beginning of the sentence, the surprise or excitement is conveyed more naturally.
4. Using Interjections in Excess
Interjections are meant to be expressive, but using too many can make your speech sound over-the-top or melodramatic. It is important to find a balance when using interjections.
For example:
-
Incorrect: “Wow, oh my God, I can’t believe this, hurray, oh no, what!”
-
Correct: “I can’t believe this. Wow, that’s incredible!”
Using one or two interjections adds emphasis without overwhelming the listener.
5. Using Inappropriate Interjections for the Situation
It’s also important to use interjections that match the context. Using a lighthearted interjection in a serious or sad situation can seem insensitive or out of place.
For example:
-
Incorrect: “Hurray, we lost the game!”
-
Correct: “Oh no, we lost the game.”
It’s essential to choose interjections that suit the emotional tone of the situation, whether it’s joy, sadness, frustration, or surprise.
How Interjections Enhance Conversations
Interjections are a valuable addition to casual conversation, adding depth and nuance to your communication. They allow speakers to react instantaneously to their environment and the people around them, enhancing the flow and emotional connection.
1. Creating Emotional Impact
By using interjections effectively, you can make your responses feel more natural and emotionally charged. Whether you’re expressing shock, joy, or sympathy, interjections bring your emotions to the forefront of the conversation.
Example:
- “Ugh, I can’t believe this is happening!”
- Here, “ugh” communicates frustration in a way that words alone cannot.
2. Engaging Your Listener
Interjections often help to grab the listener’s attention and keep them engaged. They can serve as cues that something important or surprising is about to be shared.
Example:
- “Guess what? Oh my God, I just got the job!”
- The interjection “Oh my God” highlights the excitement and adds a sense of urgency to the announcement.
3. Expressing Spontaneity
Interjections are inherently spontaneous, which is why they’re so effective at capturing the immediacy of a moment. Whether you’re shocked, happy, or in pain, interjections convey your raw, unfiltered reaction.
Example:
- “Wow, that’s a huge surprise!”
- This reflects the speaker’s genuine astonishment at the situation.
