Understanding tenses is fundamental to mastering English grammar, and the Present Perfect Continuous Tense is no exception. This tense often confuses learners, as its use blends past and present actions, creating subtle differences from other tenses like the Present Perfect. Whether you’re a student, professional, or language enthusiast, mastering the Present Perfect Continuous Tense will elevate your writing and speaking skills. In this guide, we will break down its definition, structure, uses, examples, and distinctions, ensuring you grasp it fully.
What is the Present Perfect Continuous Tense?
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense, also called the Present Perfect Progressive Tense, refers to an action that began in the past and is still ongoing or has just concluded. It conveys the duration or the repeated nature of an activity that connects the past with the present.
Definition:
The Oxford Learner’s Dictionary defines it as a tense used to express an action that started in the past and continues in the present or has recently stopped. This makes the Present Perfect Continuous Tense essential for describing actions with a focus on their duration or ongoing nature.
For example:
-
I have been reading for two hours.
-
This implies that the reading started in the past and continues up to the present moment.
-
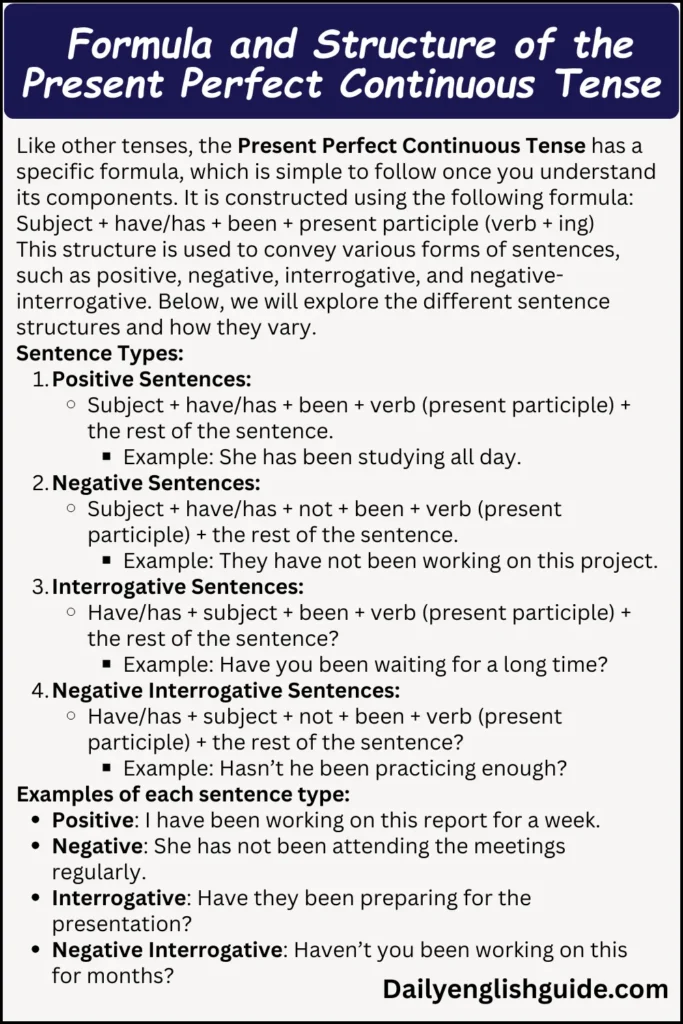
Formula and Structure of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Like other tenses, the Present Perfect Continuous Tense has a specific formula, which is simple to follow once you understand its components. It is constructed using the following formula:
This structure is used to convey various forms of sentences, such as positive, negative, interrogative, and negative-interrogative. Below, we will explore the different sentence structures and how they vary.
Sentence Types:
-
Positive Sentences:
-
Subject + have/has + been + verb (present participle) + the rest of the sentence.
-
Example: She has been studying all day.
-
-
-
Negative Sentences:
-
Subject + have/has + not + been + verb (present participle) + the rest of the sentence.
-
Example: They have not been working on this project.
-
-
-
Interrogative Sentences:
-
Have/has + subject + been + verb (present participle) + the rest of the sentence?
-
Example: Have you been waiting for a long time?
-
-
-
Negative Interrogative Sentences:
-
Have/has + subject + not + been + verb (present participle) + the rest of the sentence?
-
Example: Hasn’t he been practicing enough?
-
-
Examples of each sentence type:
-
Positive: I have been working on this report for a week.
-
Negative: She has not been attending the meetings regularly.
-
Interrogative: Have they been preparing for the presentation?
-
Negative Interrogative: Haven’t you been working on this for months?
Key Points to Remember:
-
The structure follows a consistent pattern with the helping verbs “have” or “has,” followed by “been,” and then the main verb in its continuous form (verb + ing).
-
The choice between “have” or “has” depends on the subject (singular subjects take “has,” while plural subjects take “have”).
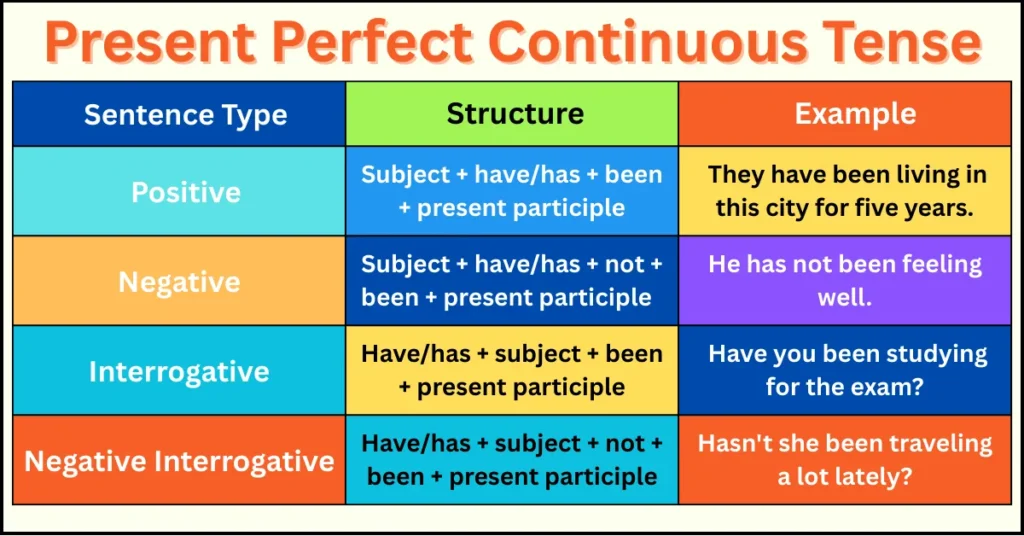
Example Table: Sentence Structure Breakdown
| Sentence Type | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | Subject + have/has + been + present participle | They have been living in this city for five years. |
| Negative | Subject + have/has + not + been + present participle | He has not been feeling well. |
| Interrogative | Have/has + subject + been + present participle | Have you been studying for the exam? |
| Negative Interrogative | Have/has + subject + not + been + present participle | Hasn’t she been traveling a lot lately? |
Once you’re familiar with the structure, it’s important to know when and how to use the Present Perfect Continuous Tense.
Uses of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense is versatile and is used in several contexts to express ongoing actions, temporary situations, and past actions that have relevance to the present. It provides a more dynamic and specific description than other tenses. Let’s explore its primary uses.
1. To Show an Action that Started in the Past and Is Still Continuing in the Present
One of the main uses of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense is to describe an action that began in the past and continues in the present. It emphasizes the duration of the activity, making it clear that the action has not yet finished.
-
Example:
-
I have been reading this book for three hours.
-
This indicates that the reading began three hours ago and is still ongoing.
-
-
-
Example:
-
She has been working at the company since 2015.
-
This suggests that her employment started in 2015 and continues to the present.
-
-
2. To Indicate a Recently Finished Action
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense can also describe an action that was happening until recently, where the action has just been completed but has a visible impact or connection to the present.
-
Example:
-
He is out of breath because he has been running.
-
This indicates that the running was happening recently, and the effect (being out of breath) is noticeable now.
-
-
-
Example:
-
I have been cleaning the kitchen, so it’s tidy now.
-
The action of cleaning was happening recently, and the present result is that the kitchen is clean.
-
-
3. To Describe Temporary or Habitual Actions
Another use of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense is to describe temporary actions or situations that are habitually repeated from the past to the present. It reflects actions or conditions that are ongoing but not permanent.
-
Example:
-
They have been staying with us while their house is being renovated.
-
The temporary nature of their stay is emphasized here, showing that it started in the past and is still in progress.
-
-
-
Example:
-
I have been working late on weekdays for the last month.
-
This example shows that the action of working late is repeated regularly during a defined period.
-
-
4. To Express Annoyance or Complaints About an Ongoing Action
In spoken English, the Present Perfect Continuous Tense can be used to express frustration or annoyance with an ongoing situation.
-
Example:
-
I have been waiting for over an hour!
-
Here, the speaker expresses irritation about the long wait.
-
-
-
Example:
-
She has been talking about the same thing all day.
-
The repetition of the action, coupled with the frustration, is conveyed through this tense.
-
-
Present Perfect Continuous vs Present Perfect
Many learners of English struggle with the difference between the Present Perfect Tense and the Present Perfect Continuous Tense. Although both tenses connect the past with the present, they serve different purposes and convey different meanings.
| Present Perfect Tense | Present Perfect Continuous Tense |
|---|---|
| Used for actions or events that started in the past and are relevant to the present. It often focuses on the result or the outcome of the action. | Used for actions that started in the past and are still continuing or were happening recently. It emphasizes the process or duration of the action. |
| Example: I have eaten lunch. (Focuses on the completion of the action.) | Example: I have been eating lunch. (Focuses on the ongoing nature or the duration of the action.) |
| It doesn’t emphasize the duration of the action. | It emphasizes how long something has been happening. |
| Example: She has finished her project. | Example: She has been working on her project for two weeks. |
Summary of Key Differences:
-
The Present Perfect Tense is about the completion of an action and its relevance to the present, while the Present Perfect Continuous Tense emphasizes the ongoing nature or the duration of an action.
-
The Present Perfect Tense answers questions like What has happened? while the Present Perfect Continuous answers What has been happening?
Understanding this distinction will help you decide which tense to use based on whether you want to highlight the result of the action (Present Perfect) or its ongoing nature (Present Perfect Continuous).
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Here are a few common mistakes learners make when using the Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
-
Using it for an action that is finished: The Present Perfect Continuous should only be used for actions that are still happening or have recently stopped. If the action is complete and has no direct connection to the present, the Present Perfect Tense is more appropriate.
-
Incorrect: I have been finished my homework.
-
Correct: I have finished my homework.
-
-
Incorrectly using “since” with a continuous action: Use “for” with the Present Perfect Continuous when referring to a period of time (e.g., days, months, years), and use “since” when referring to a specific point in time.
-
Incorrect: I have been waiting since two hours.
-
Correct: I have been waiting for two hours. or I have been waiting since 2 PM.
-
-
Omitting “been”: Remember that “been” is a crucial part of the Present Perfect Continuous structure. Omitting it leads to incorrect sentence construction.
-
Incorrect: I have working here for five years.
-
Correct: I have been working here for five years.
-
Example Table of Correct and Incorrect Usage
| Incorrect | Correct |
|---|---|
| She has been working in this company since 2019. | She has been working in this company for five years. |
| I have been to the store every day. | I have been going to the store every day. |
| They have been visiting their relatives often. | They have visited their relatives often. |
Now that you have a clear understanding of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense, its uses, and its structure, it’s time to solidify your knowledge by practicing the tense with real-life examples.
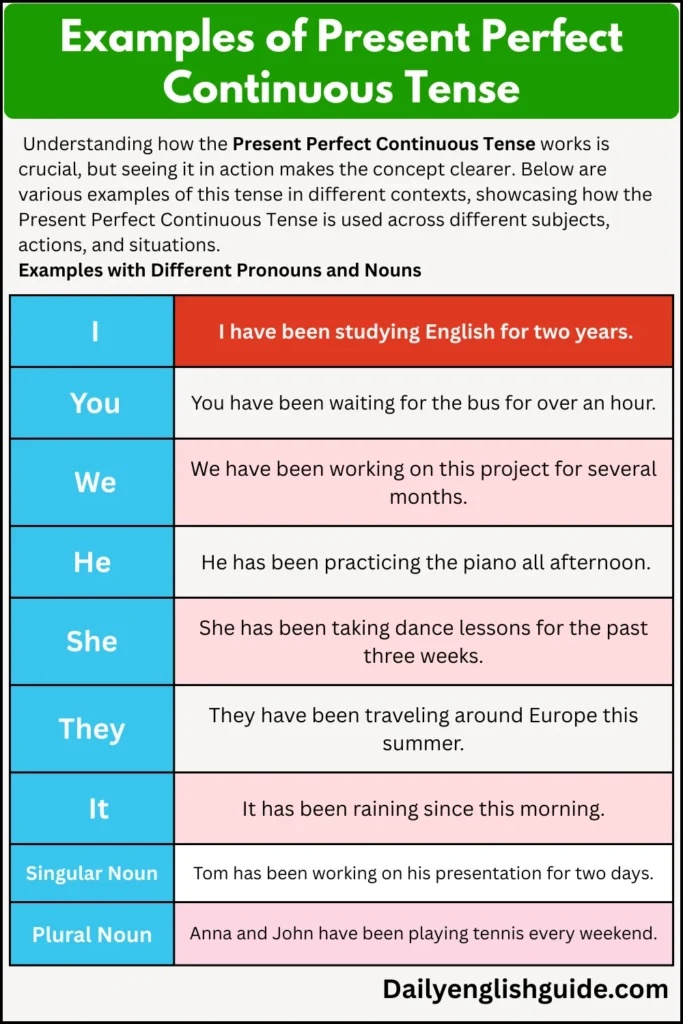
Examples of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Understanding how the Present Perfect Continuous Tense works is crucial, but seeing it in action makes the concept clearer. Below are various examples of this tense in different contexts, showcasing how the Present Perfect Continuous Tense is used across different subjects, actions, and situations.
Examples with Different Pronouns and Nouns
| Pronouns / Nouns | Examples |
|---|---|
| I | I have been studying English for two years. |
| You | You have been waiting for the bus for over an hour. |
| We | We have been working on this project for several months. |
| He | He has been practicing the piano all afternoon. |
| She | She has been taking dance lessons for the past three weeks. |
| They | They have been traveling around Europe this summer. |
| It | It has been raining since this morning. |
| Singular Noun | Tom has been working on his presentation for two days. |
| Plural Noun | Anna and John have been playing tennis every weekend. |
Each of these examples shows how the Present Perfect Continuous Tense connects past activities with the present, emphasizing the ongoing nature of the action. Notice how the tense highlights the duration of the action in each scenario.
Examples in Different Contexts
-
Work or Study:
-
I have been working on my thesis for three months.
-
This indicates a long, ongoing process.
-
-
-
Ongoing Action:
-
She has been exercising every morning to stay fit.
-
This shows that exercising has been an ongoing activity that continues regularly.
-
-
-
Temporary Situations:
-
They have been staying with relatives while their house is being renovated.
-
The action is temporary, and the situation started in the past but continues up to the present.
-
-
-
Recently Completed Action with Present Consequences:
-
He has been running, so he is tired now.
-
The action (running) has just been completed, and the result is evident in the present (being tired).
-
-
Present Perfect Continuous Tense in Different Time Frames
One of the unique features of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense is its flexibility in describing actions over different lengths of time. It can describe actions that have been occurring for a short or long duration, or actions that were happening in the very recent past. Below are examples that cover a range of time frames:
| Time Frame | Example |
|---|---|
| Short Duration | She has been reading for the last 30 minutes. |
| Medium Duration | They have been living in this city for over a year now. |
| Long Duration | I have been working as a software engineer for ten years. |
| Recent Action | I have been writing emails all morning. |
In each of these examples, the Present Perfect Continuous Tense shows that the action has started in the past and is still relevant to the present. Whether it’s a short, medium, or long duration, the tense emphasizes the process of the action.
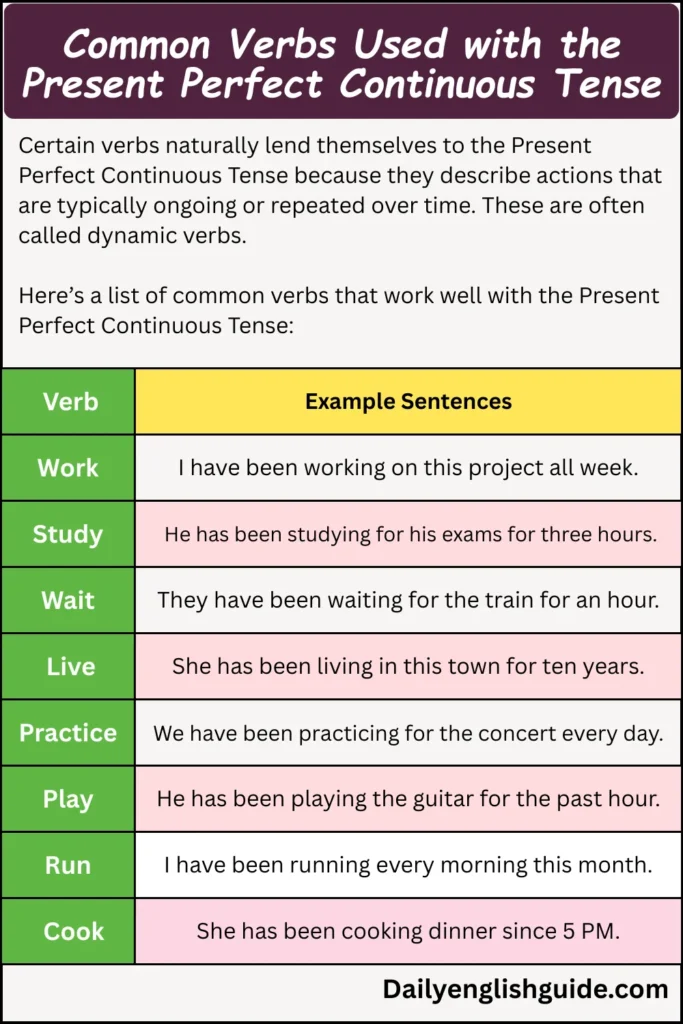
Common Verbs Used with the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Certain verbs naturally lend themselves to the Present Perfect Continuous Tense because they describe actions that are typically ongoing or repeated over time. These are often called dynamic verbs.
Here’s a list of common verbs that work well with the Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
| Verb | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| Work | I have been working on this project all week. |
| Study | He has been studying for his exams for three hours. |
| Wait | They have been waiting for the train for an hour. |
| Live | She has been living in this town for ten years. |
| Practice | We have been practicing for the concert every day. |
| Play | He has been playing the guitar for the past hour. |
| Run | I have been running every morning this month. |
| Cook | She has been cooking dinner since 5 PM. |
These dynamic verbs are ideal for describing actions that have ongoing or repeated elements, making them perfect candidates for the Present Perfect Continuous Tense.
Practice Exercises and How to Use the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
To fully master the Present Perfect Continuous Tense, it’s important to practice using it in a variety of contexts. Below are some exercises designed to help reinforce your understanding and application of this tense. The exercises focus on constructing sentences, choosing the correct verb form, and identifying mistakes.
Fill in the Blanks with the Present Perfect Continuous Form
Complete the sentences below with the correct form of the verb in parentheses.
-
I ____________ (study) for the test all day.
-
She ____________ (work) at this company for five years now.
-
We ____________ (wait) for the bus for over 30 minutes.
-
They ____________ (talk) about the movie non-stop for hours.
-
________ you ____________ (look) for your keys?
-
My friends ____________ (play) soccer every weekend for years.
-
The children ____________ (argue) since morning.
-
I ____________ (not feel) well recently.
-
We ____________ (try) to reach him, but he’s unavailable.
-
He ____________ (read) that book for over a month now.

Fill in the Blanks with the Present Perfect Continuous Form
Answers:
-
I have been studying for the test all day.
-
She has been working at this company for five years now.
-
We have been waiting for the bus for over 30 minutes.
-
They have been talking about the movie non-stop for hours.
-
Have you been looking for your keys?
-
My friends have been playing soccer every weekend for years.
-
The children have been arguing since morning.
-
I have not been feeling well recently.
-
We have been trying to reach him, but he’s unavailable.
-
He has been reading that book for over a month now.
Correcting the Mistakes in the Sentences
Read the sentences below, and identify and correct any mistakes related to the Present Perfect Continuous Tense.
-
I have been seeing him yesterday at the party.
-
They have been waiting for me when I arrived.
-
He has been never been to Japan.
-
She has been working here since five years.
-
We have been living in this city since two years.
-
I have been knowing him for a long time.
-
Have you been writing the report now?
-
He has been cooking when I arrived.
-
They have been visiting Paris last summer.
-
I have been understanding the lesson now.
Corrected Sentences:
-
I saw him yesterday at the party. (Corrected: Change to simple past tense because the action is completed.)
-
They were waiting for me when I arrived. (Corrected: Change to past continuous because the action was ongoing in the past.)
-
He has never been to Japan. (Corrected: Remove “been” after “has” and correct the word order.)
-
She has been working here for five years. (Corrected: Use “for” with duration.)
-
We have been living in this city for two years. (Corrected: Use “for” with duration.)
-
I have known him for a long time. (Corrected: Use Present Perfect tense for state verbs like “know.”)
-
Have you been writing the report? (Corrected: Proper interrogative form.)
-
He was cooking when I arrived. (Corrected: Use past continuous for an action that was ongoing in the past.)
-
They visited Paris last summer. (Corrected: Change to simple past tense as it’s a specific point in the past.)
-
I understand the lesson now. (Corrected: Change to simple present for a state of understanding.)
Identifying and Correcting Common Errors in Usage
Some common errors occur when the Present Perfect Continuous Tense is used incorrectly. Here are some common mistakes and how to fix them:
| Incorrect | Correct |
|---|---|
| She has been living in London for 2 years ago. | She has been living in London for 2 years. |
| I have been working here since 3 months. | I have been working here for 3 months. |
| They have been working in the garden now. | They have been working in the garden for hours now. |
| We have been studying English every day for 5 years. | We have been studying English every day for the past 5 years. |
As you practice, you’ll begin to see patterns in the use of this tense, which will help you avoid errors and improve fluency.
Final Summary and Key Takeaways
Mastering the Present Perfect Continuous Tense allows you to convey actions that started in the past and are still relevant in the present, emphasizing their ongoing or repeated nature. It’s perfect for talking about experiences, habits, temporary situations, and actions that have just recently concluded with lasting effects. By practicing with examples, identifying mistakes, and understanding the distinctions between similar tenses, you’ll gain confidence in using this tense appropriately.

