In English, the past tense is essential for communicating about events, actions, or situations that occurred before the present moment. Whether you’re recounting a memory, narrating a story, or simply explaining something that happened, the past tense helps you express these ideas accurately. In this article, we’ll delve deeper into what the past tense is, the types of past tenses, how to use them, and provide plenty of examples to help solidify your understanding.
What Is the Past Tense?
The past tense is a grammatical form used to describe actions or events that have already happened. In simple terms, it refers to things that occurred before the current moment. For instance, “I visited the museum yesterday” uses the past tense verb “visited” to indicate that the action of visiting the museum happened at a time prior to now.
In English, the past tense comes in various forms, and not all verbs follow a simple rule. While regular verbs form the past tense by adding “-ed” at the end, many verbs are irregular and don’t follow this pattern. This difference between regular and irregular verbs is one of the key challenges for learners of English.
The Meaning and Definition of Past Tense
The past tense allows you to speak about actions or states that occurred in the past. This can involve:
-
Completed actions: These are events that are finished, such as “She finished her homework.”
-
States of being: It can also describe a condition or situation that existed in the past, such as “He was happy yesterday.”
-
Habitual actions: In some contexts, past tense can indicate something that happened regularly in the past, for example, “We often went to the beach.”
The past tense is crucial for narration, historical writing, storytelling, and general conversation. Without it, we’d be unable to explain when things happened relative to the present.
Past Tense Definitions According to Different Dictionaries
-
Oxford Learner’s Dictionary: The past tense is defined as “the form of a verb used to describe actions in the past.”
-
Cambridge Dictionary: This dictionary states that the past tense form of the verb “is used to describe verb forms in many languages used for actions that have now finished.”
-
Merriam-Webster Dictionary: It defines the past tense as “a verb tense expressing action or state in or as if in the past.”
-
Macmillan Dictionary: According to this source, the past tense refers to “the forms of a verb group indicating that an action or event happened regularly, or that a situation existed or was true during a period before now.”
These definitions provide a clear foundation for understanding how the past tense functions in English.
Types of Past Tense
The past tense in English is not limited to a single form. There are four distinct types that convey different nuances of past actions. Understanding these types is crucial for using past tense correctly in both writing and speech.
1. Simple Past Tense
The simple past tense is used to describe actions that happened and were completed at a specific point in the past. It’s the most straightforward form of the past tense and is typically used when the exact time of the action is clear or irrelevant.
Structure:
Subject + Verb (in past form) + Rest of the sentence.
-
Example: “I visited the museum yesterday.”
-
When to use:
-
Completed actions: “She watched the movie last night.”
-
Specific time in the past: “They moved to a new house two weeks ago.”
-
Past habits or repeated actions: “When I was a child, I played outside every day.”
-
2. Past Continuous Tense
The past continuous tense, also known as the past progressive tense, is used to describe actions that were in progress at a specific moment in the past. It emphasizes the ongoing nature of an action.
Structure:
Subject + Was/Were + Verb (in -ing form) + Rest of the sentence.
-
Example: “I was reading a book when the phone rang.”
-
When to use:
-
Ongoing actions in the past: “She was studying all night.”
-
Simultaneous actions: “While I was cooking, he was cleaning the house.”
-
Actions that were interrupted: “He was walking to work when it started raining.”
-
3. Past Perfect Tense
The past perfect tense is used to describe an action that was completed before another action or event in the past. It shows the relationship between two events that happened at different times in the past.
Structure:
Subject + Had + Past participle of verb + Rest of the sentence.
-
Example: “I had finished my homework before I went to the party.”
-
When to use:
-
To show an action that was completed before another event in the past: “By the time I arrived, they had already left.”
-
To indicate a cause and effect: “She had studied hard, so she passed the exam.”
-
4. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
The past perfect continuous tense is used to emphasize the duration of an action that was ongoing in the past and was completed before another event in the past. It combines both the continuous nature of the past action and the fact that it was completed before another action.
Structure:
Subject + Had + Been + Verb (in -ing form) + Rest of the sentence.
-
Example: “I had been working for hours when she called me.”
-
When to use:
-
To show the duration of an action that was happening before another past event: “They had been waiting for an hour when the train finally arrived.”
-
To describe a past action that was interrupted: “She had been studying when her friend knocked on the door.”
-
Summary of Past Tense Types
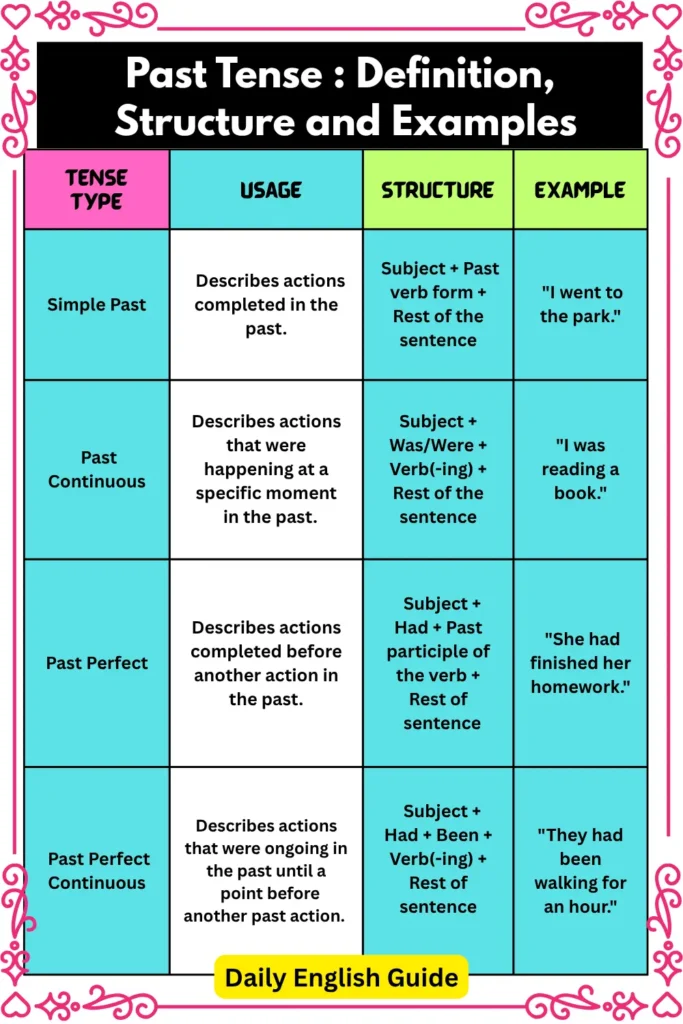
| Tense Type | Usage | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Past | Describes actions completed in the past. | Subject + Past verb form + Rest of the sentence | “I went to the park.” |
| Past Continuous | Describes actions that were happening at a specific moment in the past. | Subject + Was/Were + Verb(-ing) + Rest of the sentence | “I was reading a book.” |
| Past Perfect | Describes actions completed before another action in the past. | Subject + Had + Past participle of the verb + Rest of sentence | “She had finished her homework.” |
| Past Perfect Continuous | Describes actions that were ongoing in the past until a point before another past action. | Subject + Had + Been + Verb(-ing) + Rest of sentence | “They had been walking for an hour.” |
Understanding the Structure of Past Tense Sentences
To effectively use past tenses, it’s crucial to understand how they are structured in different types of sentences. English sentences can be categorized into four basic formats: positive, negative, interrogative, and negative interrogative. The way past tense verbs are used in these structures varies slightly, but mastering them ensures clarity and correctness.
1. Positive Sentences (Affirmative)
In positive sentences, the past tense verb is used directly after the subject. The subject performs the action in the past, and the verb remains in its past form (either regular or irregular).
Structure:
Subject + Past Tense Verb + Rest of the sentence.
-
Example: “She visited the museum last weekend.”
2. Negative Sentences
To form negative sentences in the past tense, we add the auxiliary verb “did not” or its contracted form “didn’t” before the base form of the main verb. Notice that the main verb is in its base form (infinitive), not in the past tense, because “did” already carries the past tense.
Structure:
Subject + Did not (Didn’t) + Base verb + Rest of the sentence.
-
Example: “He did not finish his homework last night.”
-
Example with contraction: “He didn’t finish his homework last night.”
3. Interrogative Sentences (Questions)
In interrogative sentences, the auxiliary verb “did” is placed at the beginning of the sentence. It is followed by the subject and then the base form of the main verb.
Structure:
Did + Subject + Base verb + Rest of the sentence.
-
Example: “Did she go to the concert last night?”
4. Negative Interrogative Sentences (Negative Questions)
Negative interrogative sentences are a combination of negative and interrogative structures. Here, “didn’t” (the contracted form of “did not”) is placed at the beginning of the sentence, followed by the subject and the base verb.
Structure:
Didn’t + Subject + Base verb + Rest of the sentence.
-
Example: “Didn’t he call you yesterday?”
Key Takeaways from Sentence Structures
-
Positive sentences use the past form of the verb directly after the subject.
-
Negative sentences require “did not” or “didn’t” plus the base verb.
-
In questions, “did” comes before the subject, followed by the base verb.
-
Negative questions are formed with “didn’t” at the beginning of the sentence.
| Sentence Type | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | Subject + Past verb + Rest of the sentence | “She visited the museum.” |
| Negative | Subject + Did not/Didn’t + Base verb + Rest of the sentence | “He didn’t finish his homework.” |
| Interrogative | Did + Subject + Base verb + Rest of the sentence | “Did she go to the concert?” |
| Negative Interrogative | Didn’t + Subject + Base verb + Rest of the sentence | “Didn’t he call you yesterday?” |

Examples of Past Tense in Different Contexts
In order to understand the practical application of the past tense, here are some real-life examples:
-
Simple Past Tense:
“They graduated from college last year.” -
Past Continuous Tense:
“I was reading a book when she called.” -
Past Perfect Tense:
“He had finished his meal before the guests arrived.” -
Past Perfect Continuous Tense:
“She had been studying for hours when her friend visited.”
Each of these examples uses a different type of past tense to convey the timing and duration of an action. By choosing the appropriate past tense, you can make your communication clearer and more specific.
FAQs About Past Tense
As with many grammar concepts, learners often have questions about how to use past tense correctly. Below are some of the most commonly asked questions regarding the past tense.
1. What is the past tense?
The past tense refers to a grammatical form used to describe actions, events, or situations that have already happened. In simple terms, it is used to express what occurred before the current moment. It can be formed by adding “-ed” to regular verbs or using the appropriate past form of irregular verbs.
2. What are the types of past tense?
There are four main types of past tense:
-
Simple Past Tense: Describes actions completed at a specific point in the past (e.g., “She visited the museum”).
-
Past Continuous Tense: Describes actions that were ongoing at a specific moment in the past (e.g., “I was reading a book”).
-
Past Perfect Tense: Describes actions completed before another action in the past (e.g., “He had finished his homework before dinner”).
-
Past Perfect Continuous Tense: Describes actions that were ongoing until a certain point in the past (e.g., “They had been waiting for an hour when the bus arrived”).
3. How do you form the past tense of regular verbs?
Regular verbs form the past tense by adding “-ed” to the base form. For example:
-
Walk → Walked
-
Play → Played
-
Talk → Talked
4. What are irregular verbs and how do they change in the past tense?
Irregular verbs do not follow the regular “-ed” rule and have unique past tense forms. For example:
-
Go → Went
-
Eat → Ate
-
See → Saw
To learn irregular verbs, it is essential to memorize their forms as they don’t follow a fixed pattern.
5. When should I use the past tense?
You should use the past tense to:
-
Describe actions or events that happened at a specific point in the past (e.g., “He left the office at 5 PM”).
-
Narrate stories, personal experiences, or historical events (e.g., “They won the game last week”).
-
Express past habits or routines (e.g., “I visited my grandmother every Sunday”).
6. What are the differences between the past perfect tense and the past perfect continuous tense?
The past perfect tense focuses on the completion of an action before another action in the past (e.g., “I had eaten before they arrived”).
The past perfect continuous tense emphasizes the duration or ongoing nature of an action that was happening before another action (e.g., “I had been working all day when she called”).
7. Can I use past tense in questions?
Yes, you can use past tense in questions by adding “did” before the subject and using the base form of the verb (e.g., “Did you go to the park yesterday?”).
Summary
Mastering the past tense is essential for effective communication in English. By understanding the different types of past tense, how to form them, and when to use them, you can significantly improve your writing and speaking skills. Whether you are narrating a story, describing past experiences, or discussing historical events, the past tense helps you convey your ideas accurately and clearly. Practice using these tenses in different contexts, and remember that consistency and correct usage will make your communication stronger.
