Common nouns are a fundamental part of the English language. They are used to name general items, people, places, or concepts, distinguishing them from proper nouns, which specify particular entities. A comprehensive understanding of common nouns is essential for grasping the broader structure of language and improving both written and spoken communication.
In this article, we’ll explore the definition of common nouns, provide various examples, discuss their types, and highlight their significance. By the end of this piece, you’ll have a thorough understanding of common nouns and their role in the English language.

What Is a Common Noun?
A common noun is a general term used to describe a person, place, thing, or idea. It refers to a category or class of objects or concepts, as opposed to a proper noun, which denotes a specific name.
Key Characteristics:
-
General Reference: Common nouns refer to general items (e.g., “book,” “city,” “dog”) rather than specific instances or names.
-
Lowercase Writing: They are typically written in lowercase unless they appear at the start of a sentence.
-
Categories: They can represent people (e.g., teacher), places (e.g., town), things (e.g., chair), or abstract concepts (e.g., happiness).
Examples:
-
Person: doctor, teacher, engineer
-
Place: country, city, village
-
Thing: table, car, phone
-
Concept: love, time, truth
Common nouns are the building blocks of sentences and form the basic structure of many everyday conversations and writings.
Common Nouns vs. Proper Nouns
One of the first distinctions you should understand about nouns is the difference between common nouns and proper nouns.
Proper Noun:
A proper noun refers to the specific name of a particular person, place, or thing and is always capitalized. For example:
-
Person: John, Mary, Einstein
-
Place: Paris, America, Mount Everest
-
Thing: Eiffel Tower, The Mona Lisa
In contrast, a common noun would be more general, like “man,” “city,” or “painting.”
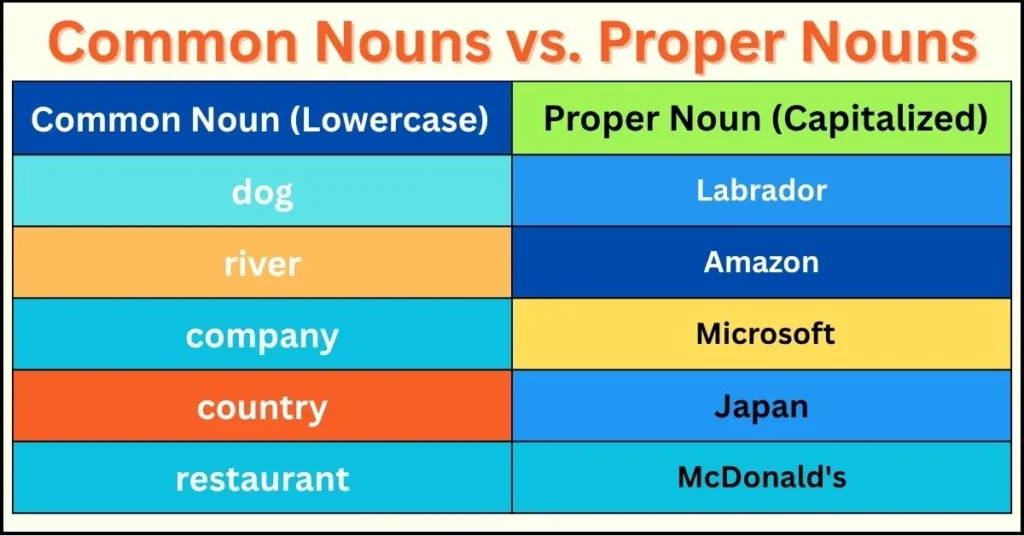
Example Table:
| Common Noun (Lowercase) | Proper Noun (Capitalized) |
|---|---|
| dog | Labrador |
| river | Amazon |
| company | Microsoft |
| country | Japan |
| restaurant | McDonald’s |
The rule to remember is simple: common nouns are general terms and are not capitalized unless they appear at the start of a sentence. Proper nouns, however, always begin with a capital letter to indicate specificity.
Why Understanding Common Nouns is Important
Understanding common nouns helps build a strong foundation in grammar. It enhances your ability to express ideas, describe objects, and tell stories. Without common nouns, sentences would lack clarity and structure.
Here are several key reasons why common nouns are crucial:
-
Sentence Structure: Common nouns help form the core of most sentences. They serve as subjects, objects, and complements.
-
Language Simplicity: They simplify communication by allowing us to generalize ideas and concepts.
-
Reading and Writing Skills: A clear understanding of common nouns aids in both reading comprehension and writing effectiveness.
-
Grammar Foundation: Learning about common nouns is one of the first steps in mastering the English language. It’s essential for learning other grammatical concepts, such as verb agreement and sentence formation.
Real-World Examples of Common Nouns
Let’s delve into a few examples where common nouns and proper nouns coexist in real-life contexts. Understanding these examples will help reinforce your grasp of common nouns.
Example 1:
-
Sentence: “I went to the park to play with my dog.”
-
Common Noun: park, dog
-
Proper Noun: none (there’s no specific name for the park or dog)
-
Example 2:
-
Sentence: “We had dinner at the restaurant, which was located in New York.”
-
Common Noun: restaurant
-
Proper Noun: New York
-
Example 3:
-
Sentence: “The teacher asked the students to write an essay about their favorite book.”
-
Common Noun: teacher, students, essay, book
-
Proper Noun: none (the teacher, students, or book aren’t specified)
-
These examples clearly illustrate the distinction between common and proper nouns in everyday sentences.
Different Types of Common Nouns
Common nouns are not just a single, uniform category; they can be broken down into several subtypes based on their function or meaning. Below are the most commonly recognized types of common nouns:
1. Abstract Nouns
Abstract nouns represent intangible concepts or ideas that cannot be touched or physically experienced.
-
Examples: love, freedom, happiness, courage
2. Concrete Nouns
Concrete nouns are things that can be perceived through the five senses. They can be seen, touched, smelled, heard, or tasted.
-
Examples: apple, table, dog, book
3. Collective Nouns
These nouns refer to groups or collections of people, animals, or things.
-
Examples: team, family, herd, group, class
4. Compound Nouns
Compound nouns are formed by combining two or more words to create a new noun.
-
Examples: toothpaste, basketball, swimming pool, mother-in-law
5. Countable Nouns
Countable nouns are those that can be counted and have both singular and plural forms.
-
Examples: book (books), car (cars), idea (ideas)
6. Uncountable (Mass) Nouns
Uncountable nouns refer to substances or concepts that cannot be counted individually.
-
Examples: water, rice, air, information
7. Gender-Specific Nouns
These nouns specifically refer to male or female entities.
-
Examples: waiter, waitress; king, queen; actor, actress

How to Identify and Use Common Nouns Effectively
Identifying common nouns in a sentence is an essential skill for understanding the structure of language. Let’s explore some practical strategies to identify common nouns in everyday writing and speech.
Steps to Identify Common Nouns
-
Look for General Terms: Common nouns refer to general categories of things, so start by looking for words that could apply to a wide range of objects, people, places, or ideas.
-
Check for Lowercase: Common nouns are typically written in lowercase unless they start a sentence or are part of a title.
-
Exclude Specific Names: Proper nouns are capitalized and refer to specific entities. If the word names something specific, it’s a proper noun, not a common noun.
-
Test with Substitution: Try substituting the noun with another word that refers to a similar category. For example, replace “dog” with “cat” or “book” with “notebook” to check if it remains a general term.
Example Exercise
-
Sentence: “The teacher handed me the book.”
-
Common Nouns: teacher, book
-
Explanation: The word “teacher” refers to any teacher, not a specific one, and “book” refers to any book.
-
Identifying common nouns is crucial for improving sentence construction and ensuring clarity in your writing. Understanding their usage allows you to craft more coherent and organized content.
Common Nouns and Sentence Construction
In English, common nouns are often used as subjects, objects, and complements in sentences. Here’s how common nouns function in different parts of a sentence:
Common Nouns as Subjects
A subject is the noun that performs the action or is described in a sentence. Common nouns can serve as the subject of a sentence.
-
Example: “The cat chased the mouse.”
-
Here, the common noun “cat” is the subject that is performing the action.
-
Common Nouns as Objects
An object is the noun that receives the action of the verb. Common nouns often appear as objects in sentences.
-
Example: “She threw the ball.”
-
“Ball” is the common noun acting as the object of the verb “threw.”
-
Common Nouns as Complements
A complement completes the meaning of the subject or object. It provides additional information about a noun.
-
Example: “The teacher is an expert.”
-
“Expert” is a common noun that complements “teacher.”
-
Knowing how to use common nouns effectively can improve your sentence variety and make your writing more engaging.
Common Noun Categories in Detail
While we’ve briefly covered various types of common nouns, let’s dive deeper into each category to better understand their nuances. Here’s a detailed look at each type of common noun and examples of how to use them.
1. Abstract Nouns
Abstract nouns are ideas or concepts that you cannot touch or see. These nouns refer to emotions, qualities, or states of being. They are often used to describe feelings or states that exist in a more intellectual or philosophical realm.
-
Examples: happiness, freedom, love, anger, bravery, honesty
-
Sentence Example: “The love between them was undeniable.”
2. Concrete Nouns
Concrete nouns refer to objects or things that can be physically touched, seen, smelled, or heard. These are tangible items that exist in the physical world.
-
Examples: book, table, dog, flower, car, tree
-
Sentence Example: “She placed the flower on the table.”
3. Collective Nouns
Collective nouns refer to groups of people, animals, or things. These nouns allow us to describe multiple entities as a single unit.
-
Examples: team, family, flock, audience, crowd
-
Sentence Example: “The team celebrated their victory.”
4. Compound Nouns
Compound nouns are created by combining two or more words to form a new word. They can be written as one word, two words, or hyphenated, depending on their usage.
-
Examples: basketball, toothpaste, mother-in-law, hairbrush
-
Sentence Example: “He wore a basketball jersey.”
5. Countable Nouns
Countable nouns are things that can be counted, and they have both singular and plural forms. You can easily add an “s” or “es” to make them plural.
-
Examples: book (books), chair (chairs), apple (apples)
-
Sentence Example: “I have two books on my desk.”
6. Uncountable Nouns
Uncountable nouns refer to things that cannot be counted individually. They represent mass, liquids, or abstract concepts that cannot be easily quantified.
-
Examples: water, sugar, sand, information, music
-
Sentence Example: “She loves to listen to music while studying.”
7. Gender-Specific Nouns
Gender-specific nouns refer to people or animals that are male or female. These nouns distinguish between the two genders.
-
Examples: waiter (waitress), king (queen), actor (actress)
-
Sentence Example: “The waiter served our meal promptly.”
The Role of Common Nouns in Everyday Language
Common nouns play a significant role in both spoken and written communication. They form the foundation of how we describe the world around us, communicate ideas, and interact with others. Understanding their usage and categorization is crucial for improving fluency and accuracy in English.
In Spoken Language:
In conversation, common nouns allow us to talk about general things without having to specify every detail. For instance, when discussing the weather, instead of referring to a specific type of cloud, we might say “cloud” as a general term, which makes the conversation more efficient.
In Writing:
In written language, common nouns help create vivid descriptions and clear explanations. For example, in storytelling, authors use common nouns to provide context and help the reader visualize the scenes.
Common Nouns in Different Contexts
Common nouns are versatile and can be used in various contexts, including formal writing, informal conversations, and creative works. Understanding how to use them appropriately in different situations is essential for effective communication.
Common Nouns in Formal Writing
In formal writing, such as academic papers, business communications, and professional reports, common nouns are used to convey precise and clear information. Since formal writing often aims to inform, persuade, or present research, common nouns help maintain objectivity and clarity.
-
Examples: report, study, analysis, conclusion, data
-
Sentence Example: “The study revealed significant findings in the area of environmental conservation.”
When using common nouns in formal writing, ensure that they remain general and avoid unnecessary specificity unless required for the context. For example, instead of writing “the beautiful forest,” use “the forest” unless the beauty of the forest is the subject of discussion.
Common Nouns in Informal Language
In informal language, common nouns are used to describe everyday objects, people, or actions. These nouns are integral to casual conversations, social media posts, personal blogs, and text messages.
-
Examples: friend, party, vacation, movie, food
-
Sentence Example: “I had a great time at the party last night!”
In informal writing, the tone tends to be more relaxed, and the language used can be more descriptive. Common nouns here help to create a friendly, approachable atmosphere.
Common Nouns in Creative Writing
Creative writing, including poetry, fiction, and storytelling, also relies on common nouns to describe characters, settings, and objects. Writers use common nouns to evoke emotions and build rich, detailed worlds. In creative writing, the use of descriptive common nouns can make the text more engaging and vivid.
-
Examples: hero, journey, battle, home, sky
-
Sentence Example: “The hero embarked on a perilous journey across the vast desert.”
While common nouns serve a descriptive purpose in creative works, writers often complement them with adjectives and other parts of speech to add depth and color.
Common Noun Errors to Avoid
Even though common nouns are simple and essential, there are a few common mistakes that people make when using them. Let’s take a look at some of the errors to avoid:
1. Capitalizing Common Nouns
One of the most frequent mistakes people make is capitalizing common nouns when they don’t need to. Remember, common nouns are not capitalized unless they appear at the start of a sentence or are part of a proper noun.
-
Incorrect: “I went to the School.”
-
Correct: “I went to the school.”
2. Confusing Common and Proper Nouns
Sometimes, it’s easy to mistake common nouns for proper nouns, especially when we’re talking about specific places, organizations, or items. Always check if the noun refers to a specific name or is simply a general term.
-
Incorrect: “I visited the Amazon river.”
-
Correct: “I visited the amazon river.” (Note: Amazon is a proper noun when referring to the specific river, but amazon is a common noun when referring to the broader category of rivers.)
3. Overusing Common Nouns
While common nouns are important, using too many in one sentence can make the writing repetitive and bland. Try to vary your sentence structure and vocabulary to make your writing more engaging.
-
Incorrect: “The dog was sitting on the dog bed in the dog house.”
-
Correct: “The dog sat comfortably on its bed inside the house.”
To avoid overuse, consider replacing repetitive common nouns with pronouns or synonyms when appropriate.
Conclusion
Common nouns are an essential aspect of the English language. They help us name and categorize the world around us, whether we’re referring to people, places, things, or abstract concepts. Understanding the nuances of common nouns, including their various types and proper usage, allows for clearer and more effective communication.
