Adjectives are words that describe nouns. Opposite adjectives, in particular, are word pairs that express contrasting qualities, helping to define the difference between two things. These pairs are not only useful in everyday conversation but also play a critical role in writing, literature, and various fields of study. Learning opposite adjectives allows you to build a richer vocabulary, making it easier to describe people, objects, or situations more effectively.
What Are Opposite Adjectives?
Opposite adjectives refer to pairs of adjectives that describe two extreme qualities or conditions. The most commonly used opposite adjectives are pairs like “big and small,” “happy and sad,” or “hot and cold.” By understanding these opposites, you can compare and contrast different characteristics more easily, making your communication more precise.

Opposite Adjectives List
Size and Dimension
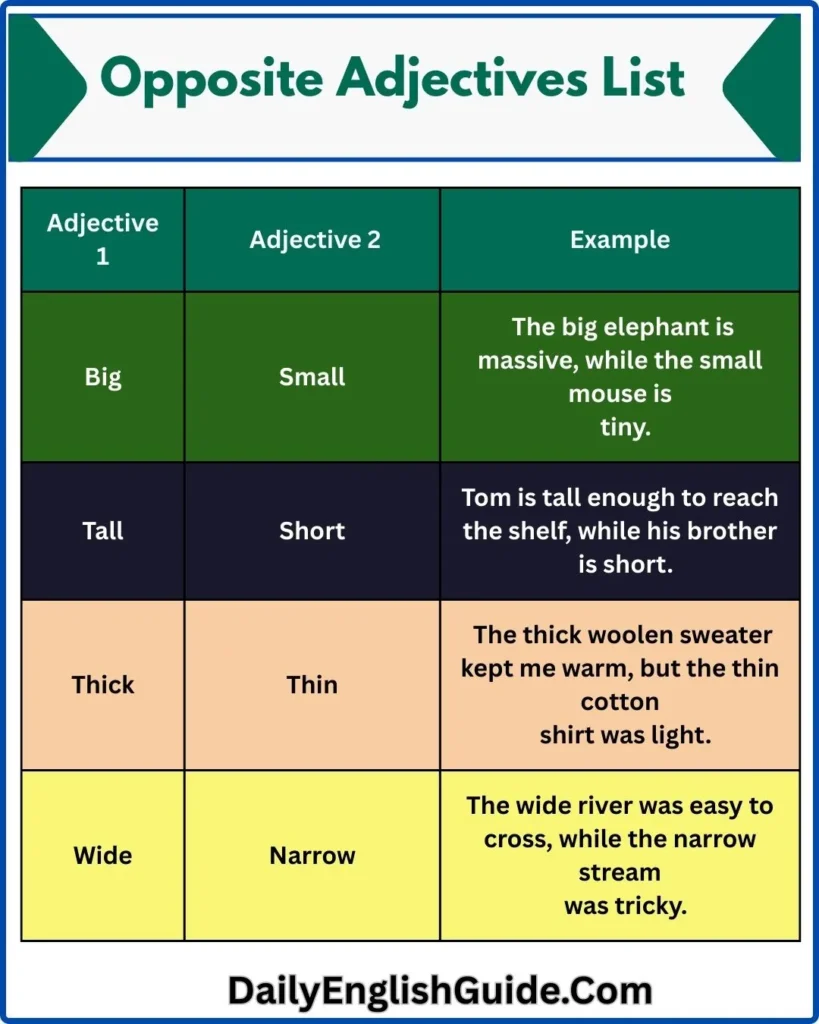
| Adjective 1 | Adjective 2 | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Big | Small | The big elephant is massive, while the small mouse is tiny. |
| Tall | Short | Tom is tall enough to reach the shelf, while his brother is short. |
| Thick | Thin | The thick woolen sweater kept me warm, but the thin cotton shirt was light. |
| Wide | Narrow | The wide river was easy to cross, while the narrow stream was tricky. |
Speed and Time
| Adjective 1 | Adjective 2 | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Fast | Slow | The fast car zoomed ahead, while the slow bus was left behind. |
| Early | Late | We arrived early at the event, but many guests showed up late. |
| Quick | Delayed | The quick response from the team saved the project, while the delayed one caused issues. |
| Prompt | Tardy | The prompt service impressed us, but the tardy one made us wait. |
Appearance
| Adjective 1 | Adjective 2 | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Beautiful | Ugly | The beautiful landscape was breathtaking, while the ugly building stood out. |
| Clean | Dirty | The clean room was organized, while the dirty kitchen needed cleaning. |
| Bright | Dim | The bright sunlight lit up the room, while the dim light created shadows. |
| Neat | Messy | The neat desk made it easy to work, but the messy one was hard to focus on. |
Temperature
| Adjective 1 | Adjective 2 | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Hot | Cold | The hot tea warmed my hands, but the cold drink was refreshing. |
| Dry | Wet | The dry desert was dusty, while the wet rainforest was lush and green. |
| Warm | Freezing | The warm blanket kept me cozy, but the freezing air outside made me shiver. |
| Boiling | Chilly | The boiling water was perfect for tea, but the chilly wind was unbearable. |
Personality and Emotion
| Adjective 1 | Adjective 2 | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Happy | Sad | He was happy with the news, but she felt sad about missing out. |
| Brave | Cowardly | The brave soldier faced danger, while the cowardly one hid behind cover. |
| Generous | Selfish | She was generous with her time, while he was selfish and never shared. |
| Friendly | Unfriendly | The friendly dog welcomed everyone, while the unfriendly cat hid away. |

Strength and Weakness
| Adjective 1 | Adjective 2 | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Strong | Weak | The strong athlete lifted the weights, but the weak one struggled. |
| Powerful | Feeble | The powerful engine roared to life, but the feeble motor sputtered. |
| Sturdy | Fragile | The sturdy chair supported my weight, but the fragile vase broke easily. |
| Tough | Delicate | The tough exterior protected the machine, but the delicate components were easily damaged. |
Richness and Poverty
| Adjective 1 | Adjective 2 | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Wealthy | Poor | The wealthy businessman owned many homes, while the poor man struggled. |
| Affluent | Impoverished | The affluent neighborhood had beautiful homes, while the impoverished area lacked basic amenities. |
| Luxurious | Simple | The luxurious hotel had all the amenities, while the simple cottage was more modest. |
| Rich | Needy | The rich family vacationed in luxury, while the needy family had little. |
Size and Shape
| Adjective 1 | Adjective 2 | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Large | Tiny | The large house had many rooms, but the tiny apartment was cozy. |
| Big | Small | The big dog was intimidating, but the small one was friendly. |
| Wide | Slim | The wide river was difficult to cross, while the slim stream was easier. |
| Bulky | Petite | The bulky coat kept me warm, while the petite scarf was light. |
Cleanliness and Disorder
| Adjective 1 | Adjective 2 | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Organized | Disorganized | The organized office was neat and tidy, while the disorganized desk was a mess. |
| Tidy | Messy | The tidy living room looked inviting, while the messy bedroom was chaotic. |
| Pristine | Grimy | The pristine beaches were untouched, but the grimy alley was dirty. |
| Spotless | Dirty | The spotless bathroom was sparkling clean, but the dirty kitchen needed attention. |
Health and Condition
| Adjective 1 | Adjective 2 | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy | Sick | She felt healthy after the workout, but he felt sick after the flu. |
| Fit | Unfit | The fit athlete ran a marathon, while the unfit person struggled. |
| Energetic | Lethargic | She felt energetic in the morning, but lethargic in the afternoon. |
| Robust | Weak | The robust tree withstood the storm, while the weak plant collapsed. |
Categories of Opposite Adjectives
Opposite adjectives can be categorized based on what they describe. These categories help to organize adjectives in a way that is easier to understand and use in various contexts. Below, we break down some common categories of opposite adjectives with examples.
1. Opposites for Size
Size is one of the most fundamental qualities that we compare when using opposite adjectives. Whether it’s the size of an object, a person, or a space, opposite adjectives help you convey the scale accurately.
Examples:
-
Big vs. Small
-
Big refers to something large in size.
-
Small means something little or compact in size.
-
Example: The big house is spacious, while the small cottage feels cozy.
-
-
Tall vs. Short
-
Tall means having a greater height.
-
Short refers to less height.
-
Example: Hiba is tall enough to reach the top shelf, but her sister is short and needs a stool.
-
-
Thick vs. Thin
-
Thick describes something that has great width or density.
-
Thin refers to something with little width or density.
-
Example: The thick woolen sweater kept me warm, but the thin cotton shirt wasn’t enough.
-
2. Opposites for Speed and Time
Opposite adjectives related to speed and time allow us to describe how quickly something happens or how punctual someone is. These words help to give a sense of urgency or delay in both actions and events.
Examples:
-
Fast vs. Slow
-
Fast means quick in movement or action.
-
Slow refers to taking a long time to complete something.
-
Example: The fast car zoomed past, but the slow-moving truck blocked the road.
-
-
Early vs. Late
-
Early means happening or arriving before the expected time.
-
Late refers to arriving or happening after the expected time.
-
Example: We arrived early at the event, but many guests arrived late due to traffic.
-
3. Opposites for Appearance
When it comes to describing appearance, opposite adjectives are crucial for conveying how things look. These adjectives can describe people, places, or objects and help you express a broad range of visual contrasts.
Examples:
-
Beautiful vs. Ugly
-
Beautiful means aesthetically pleasing or attractive.
-
Ugly means unpleasant to look at or unattractive.
-
Example: The beautiful garden was filled with vibrant flowers, but the alley was ugly and neglected.
-
-
Clean vs. Dirty
-
Clean refers to something neat, free from dirt or mess.
-
Dirty means something unclean or soiled.
-
Example: The kitchen is clean, but the garage is dirty with clutter everywhere.
-
4. Opposites for Temperature
Temperature is another area where opposite adjectives are commonly used. Whether you’re describing the weather, an object, or even emotions, these pairs provide the clarity needed to describe contrasting temperatures.
Examples:
-
Hot vs. Cold
-
Hot means having a high temperature.
-
Cold refers to a low temperature.
-
Example: The summer afternoon was hot, but the winter morning was cold with a biting wind.
-
-
Dry vs. Wet
-
Dry means lacking moisture or water.
-
Wet refers to something covered with or saturated by water.
-
Example: The desert was dry and arid, but the rainforest was wet and humid.
-
5. Opposites for Emotions and Personality
Describing feelings and personality traits is one of the most important uses of opposite adjectives. Whether you’re discussing a person’s mood or characteristics, opposite adjectives help you contrast different emotional states and personality traits.
Examples:
-
Happy vs. Sad
-
Happy refers to feeling good or joyful.
-
Sad means feeling down or unhappy.
-
Example: Hassan was happy after receiving good news, while Sarah felt sad because of a loss.
-
-
Brave vs. Cowardly
-
Brave means showing courage in difficult situations.
-
Cowardly refers to lacking bravery or avoiding danger out of fear.
-
Example: Zainab showed bravery by speaking in front of a large audience, while Omar acted cowardly and hesitated.
-
-
Generous vs. Selfish
-
Generous refers to being willing to share or give.
-
Selfish means being concerned only with one’s own needs or desires.
-
Example: Ali is generous, often sharing his food with others, while Sara is selfish and only thinks of herself.
-
How to Use Opposite Adjectives in Sentences
Opposite adjectives are commonly used to create comparisons or contrasts within sentences. They are often paired with conjunctions like but, while, or however to emphasize the differences. Using them correctly can improve the clarity and impact of your communication.
Common Usage Tips:
-
Use “but” or “while” to compare opposites:
-
Example: The sky is bright, but the ground is dark.
-
-
Keep adjectives close to the nouns they modify to avoid confusion.
-
Example: The cold ice and the hot water mixed together.
-
Correct vs. Incorrect Usage:
-
Correct: “Aisha’s dress is long, but Zainab’s dress is short.”
-
Incorrect: “Aisha’s dress is long, and Zainab’s dress is long too.”
By following these guidelines, you can use opposite adjectives in a way that enhances the clarity and expressiveness of your writing.
