Parts of speech are the fundamental building blocks of grammar. They define the role of each word in a sentence, helping to create meaning, structure, and flow. Whether you’re writing, speaking, or reading, understanding parts of speech is essential for mastering the English language.
In this article, we will delve deep into the different types of parts of speech, offering clear definitions, detailed examples, and practical usage tips. This guide will serve as a comprehensive resource, designed for students, grammar enthusiasts, and professionals alike. We’ll also examine how parts of speech function together to form coherent and effective communication.
What Is a Part of Speech?
A part of speech is a category of words that have similar grammatical properties. In English, the role a word plays in a sentence helps determine its part of speech. Words can serve more than one function depending on their usage, which is why mastering parts of speech is vital for understanding how sentences are constructed.
Parts of Speec
Words can be classified into eight distinct categories based on their roles:
-
Nouns
-
Pronouns
-
Verbs
-
Adverbs
-
Adjectives
-
Prepositions
-
Conjunctions
-
Interjections
Each part of speech has a unique function, and the way they are used can change the meaning of a sentence.
Breaking Down the 8 Parts of Speech
Let’s explore each part of speech in detail, examining definitions, categories, and practical examples.
1. Nouns
Definition:
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, idea, or animal. Nouns are the foundation of most sentences and typically serve as the subject or object of a sentence.
Types of Nouns
-
Common Nouns: General names for things (e.g., car, city, teacher).
-
Proper Nouns: Specific names of people, places, or things (e.g., Sarah, Paris, Mount Everest).
-
Abstract Nouns: Names for things that cannot be touched or seen (e.g., love, freedom, happiness).
-
Collective Nouns: Words for groups or collections (e.g., team, family, audience).
Examples of Nouns in Sentences
-
She visited Paris last year. (Proper Noun)
-
The team played excellently. (Collective Noun)
-
Happiness is the key to success. (Abstract Noun)
2. Pronouns
Definition:
A pronoun is a word used to replace a noun in a sentence, usually to avoid repetition. Pronouns help make sentences more concise and clear.
Types of Pronouns
-
Personal Pronouns: Refers to a specific person or thing (e.g., he, she, it, they).
-
Possessive Pronouns: Indicate ownership (e.g., mine, yours, his, hers).
-
Reflexive Pronouns: Refer back to the subject of the sentence (e.g., myself, yourself, themselves).
-
Relative Pronouns: Connect clauses or phrases to nouns (e.g., who, which, that).
-
Demonstrative Pronouns: Point to specific things (e.g., this, that, these, those).
Examples of Pronouns in Sentences
-
She is going to the store. (Personal Pronoun)
-
This book is mine. (Possessive Pronoun)
-
He completed the task himself. (Reflexive Pronoun)
-
The car that I bought is blue. (Relative Pronoun)

3. Verbs
Definition:
A verb is a word that expresses an action or state of being. Verbs are essential for forming sentences because they tell what the subject is doing or what is happening to the subject.
Types of Verbs
-
Action Verbs: Describe an action (e.g., run, jump, swim).
-
Linking Verbs: Connect the subject to a subject complement (e.g., is, are, was).
-
Auxiliary Verbs (Helping Verbs): Help the main verb express time, mood, or voice (e.g., have, will, can).
Examples of Verbs in Sentences
-
She runs every morning. (Action Verb)
-
He is a teacher. (Linking Verb)
-
I have finished my homework. (Auxiliary Verb)
4. Adverbs
Definition:
An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb. It often tells us how, when, where, or to what degree something happens.
Types of Adverbs
-
Adverbs of Manner: Describe how an action is performed (e.g., quickly, slowly, carefully).
-
Adverbs of Time: Indicate when an action takes place (e.g., now, later, soon).
-
Adverbs of Place: Describe where an action happens (e.g., here, there, everywhere).
-
Adverbs of Frequency: Tell us how often something happens (e.g., always, often, never).
-
Adverbs of Degree: Show the intensity or extent of an action (e.g., very, too, quite).
Examples of Adverbs in Sentences
-
She sings beautifully. (Adverb of Manner)
-
I will call you soon. (Adverb of Time)
-
The dog runs everywhere. (Adverb of Place)
5. Adjectives
Definition:
An adjective is a word that describes or gives more information about a noun or pronoun. Adjectives help clarify the qualities, size, color, or state of the noun they modify.
Types of Adjectives
-
Descriptive Adjectives: Describe the qualities or characteristics of a noun (e.g., beautiful, tall, round).
-
Quantitative Adjectives: Indicate the quantity of a noun (e.g., some, many, few).
-
Demonstrative Adjectives: Specify which noun is being referred to (e.g., this, those, that).
-
Possessive Adjectives: Show ownership (e.g., my, his, her).
-
Interrogative Adjectives: Ask questions about nouns (e.g., which, what, whose).
Examples of Adjectives in Sentences
-
The small dog barked loudly. (Descriptive Adjective)
-
I have many books on my shelf. (Quantitative Adjective)
-
That book is mine. (Demonstrative Adjective)
6. Prepositions
Definition:
A preposition is a word that links nouns, pronouns, or phrases to other words in a sentence. Prepositions show the relationship between the object and other parts of the sentence, often indicating time, place, or direction.
Types of Prepositions
-
Prepositions of Time: Indicate when something happens (e.g., at, on, during).
-
Prepositions of Place: Show the location of something (e.g., in, under, between).
-
Prepositions of Direction/Movement: Indicate movement from one place to another (e.g., to, into, towards).
-
Prepositions of Agent/Instrument: Show the tool or agent involved in the action (e.g., by, with).
Examples of Prepositions in Sentences
-
She is sitting on the chair. (Preposition of Place)
-
We met at the park. (Preposition of Time)
-
He walked into the room. (Preposition of Direction)
7. Conjunctions
Definition:
A conjunction is a word that connects clauses, phrases, or words in a sentence. Conjunctions are crucial for forming complex sentences and showing the relationships between ideas.
Types of Conjunctions
-
Coordinating Conjunctions: Link words, phrases, or clauses of equal importance (e.g., and, but, or, nor, for, yet, so).
-
Subordinating Conjunctions: Join a dependent clause with an independent clause (e.g., because, although, if, unless).
-
Correlative Conjunctions: Work in pairs to link equal elements (e.g., either…or, neither…nor, both…and).
Examples of Conjunctions in Sentences
-
I wanted to go, but I was too tired. (Coordinating Conjunction)
-
She stayed home because it was raining. (Subordinating Conjunction)
-
Either you study hard, or you will fail. (Correlative Conjunction)
8. Interjections
Definition:
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses strong emotions or sudden reactions. Interjections are often followed by an exclamation mark and can stand alone in a sentence.
Types of Interjections
-
Emotional Interjections: Express feelings or reactions (e.g., wow, alas, yippee).
-
Grammatical Interjections: Express mild emotions or fill pauses in speech (e.g., well, oh, hmm).
Examples of Interjections in Sentences
-
Wow! That was an amazing performance. (Emotional Interjection)
-
Oh, I forgot to call her. (Grammatical Interjection)
Summary of the 8 Parts of Speech
To recap, the 8 parts of speech are essential components of the English language. Each part serves a unique role in constructing meaningful and grammatically correct sentences. Here’s a quick summary:
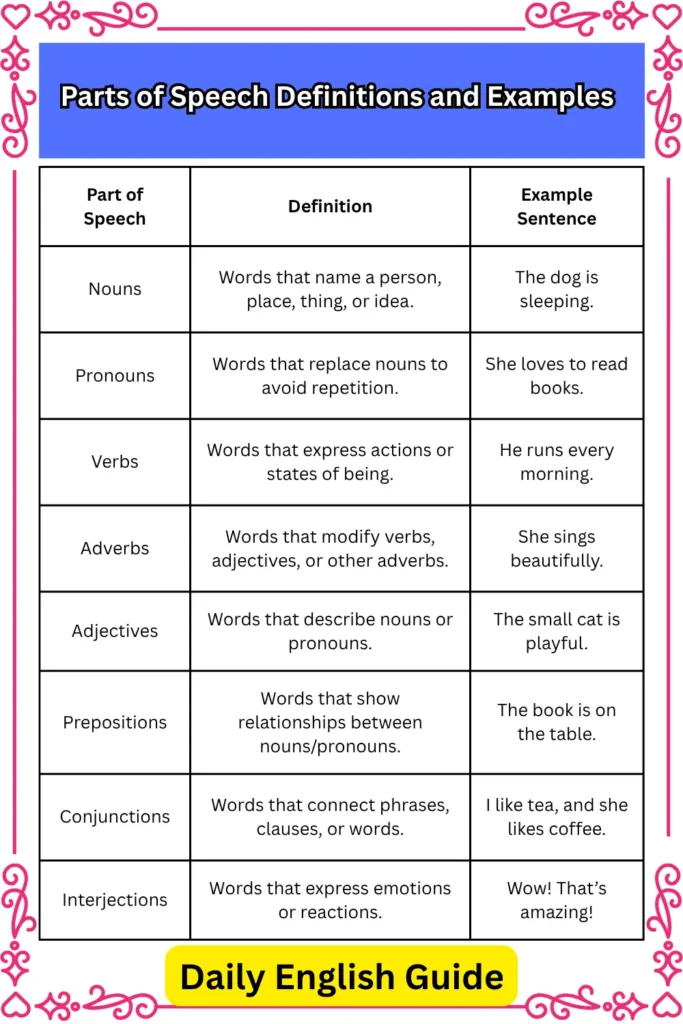
| Part of Speech | Definition | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Nouns | Words that name a person, place, thing, or idea. | The dog is sleeping. |
| Pronouns | Words that replace nouns to avoid repetition. | She loves to read books. |
| Verbs | Words that express actions or states of being. | He runs every morning. |
| Adverbs | Words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. | She sings beautifully. |
| Adjectives | Words that describe nouns or pronouns. | The small cat is playful. |
| Prepositions | Words that show relationships between nouns/pronouns. | The book is on the table. |
| Conjunctions | Words that connect phrases, clauses, or words. | I like tea, and she likes coffee. |
| Interjections | Words that express emotions or reactions. | Wow! That’s amazing! |
